Corneal Abrasion
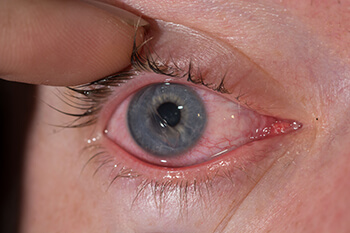 The cornea is the clear front window of the eye. It is covered by a layer of skin called the epithelium.
The cornea is the clear front window of the eye. It is covered by a layer of skin called the epithelium.
An abrasion is a scratch.
When the skin of the cornea gets scratched (usually from an injury), the nerve endings just beneath the skin become exposed. This causes significant pain, as well as redness, tearing, and sensitivity to light. These symptoms will gradually improve as the skin heals back over the cornea.
While the scratch is healing, there is an increased risk of an infection of the cornea. Therefore, it is important to use an antibiotic eye drop or ointment during the healing process. Ointments tend to be more soothing to the eye compared to drops, but their thicker consistency causes worse blurry vision compared to drops.
Your symptoms should be completely resolved within 2 weeks. If you experience worsening pain, redness, or light sensitivity – or if you begin having thick (as opposed to watery) discharge – you should call our clinic immediately.
After they are healed, corneal abrasions do not result in scars or permanent changes to vision. However, it is possible that the new skin covering the scratch does not stick down to the cornea as tightly as it should. If this occurs, the skin can be more easily disrupted, and the original symptoms can recur. This is known as “Recurrent Erosion Syndrome.” The bad news is that there is no way to predict which patients will have this problem. The good news is that it can be treated.
Visit the American Academy of Ophthalmology’s EyeSmart® website to learn more about Corneal Abrasions.